With the increase in cyber threats and government surveillance, many users are looking for ways to protect their personal information and keep their online activities secure.
Two of the most popular tools to achieve these goals are Tor and VPN. Do you know the difference?
Despite having similar purposes, Tor and VPN work in different ways and offer different levels of protection and convenience.
This article aims to clarify these differences, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each tool, and help you determine which is the best option for your specific privacy and online security needs.
👉 PREMIUM VPN ON SALE THIS WEEK →
What is Tor?
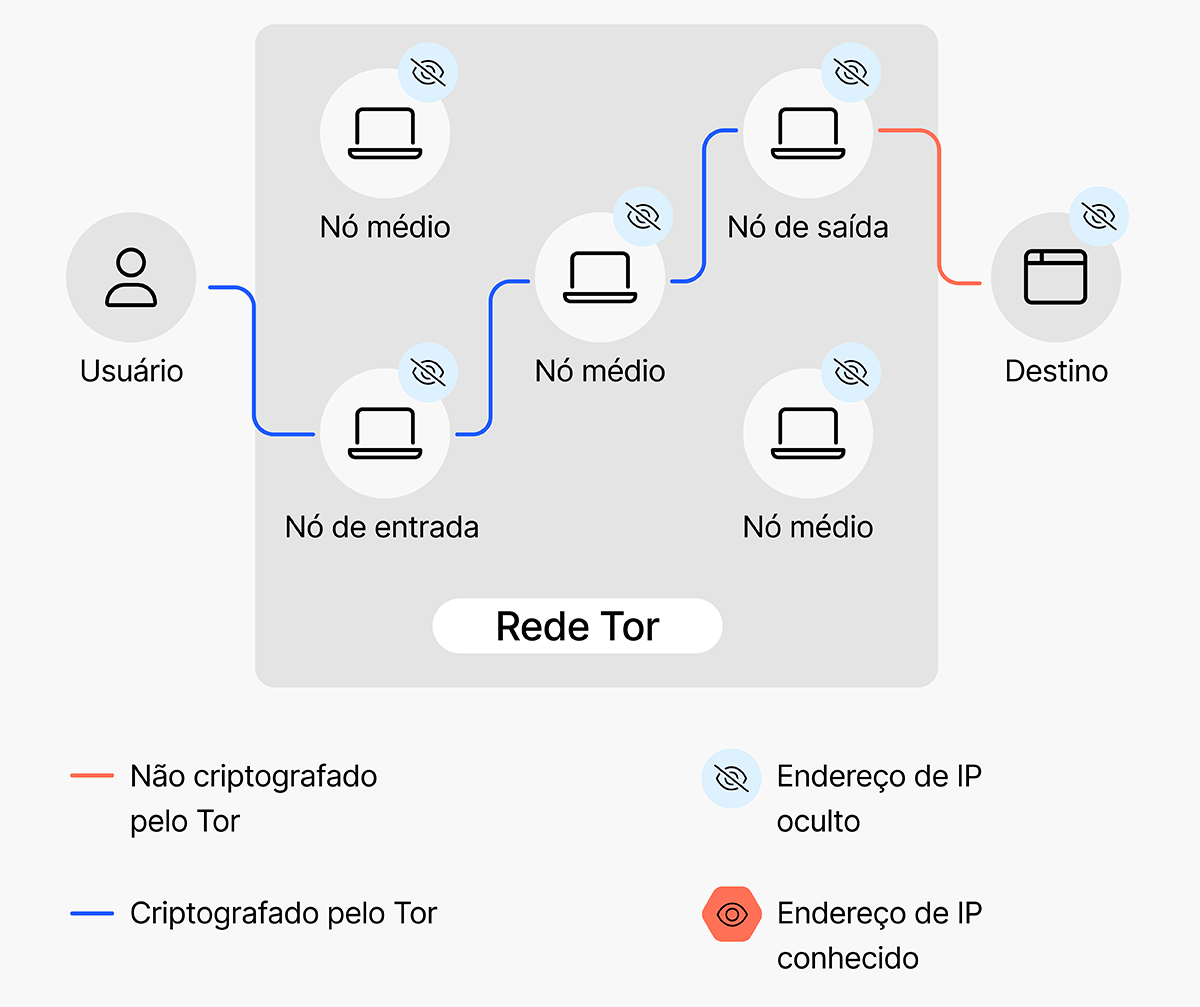
Tor, short for The Onion Router, is a free and open-source network that aims to provide anonymity to its users on the internet.
Maintained by The Tor Project, a non-profit organization, Tor is financially supported by NGOs and companies like Google.
The main feature of Tor is its ability to hide the user’s identity by encrypting their browsing requests and routing them through a series of volunteer servers, called relays.
✅ Advantages of Tor
- Free and easy to use: Tor is completely free and can be used by anyone with minimal technical knowledge.
- Robust anonymity: The multi-layer encryption technique ensures a high level of anonymity for most users.
- Resilience to disruption: The extensive network of volunteer servers makes it difficult for any entity to intercept or disrupt the functioning of Tor.
- Access to the Dark Web: Tor allows access to .onion sites, which are not available through common browsers.
❌ Disadvantages of Tor
- Vulnerability at the exit node: The user’s request leaves the exit node unencrypted, which can allow interception by the ISP or government authorities.
- Reduced speed: The process of multi-layer encryption and routing through multiple servers can slow down the connection.
- Lack of transparency: The accountability and transparency of relay operators are difficult to verify, which can pose a potential risk.
- Difficulty obtaining a specific IP: Obtaining an IP from a specific country can be challenging and may require several reconnection attempts.
- Risks on the Dark Web: Browsing .onion sites can be dangerous if not done carefully.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a service that encrypts all user traffic and routes it through a secure tunnel, providing anonymity and online security.
Premium VPN providers adopt strict “No logs” policies, ensuring that no information about users’ online activities is stored.
VPNs use different security protocols, such as WireGuard, OpenVPN, and IKEv2/IPsec, to ensure a secure connection.
✅ Advantages of a VPN
- High speed: Modern protocols like WireGuard ensure excellent connection speeds.
- Transparency and accountability: It’s easy to identify who operates the VPN service, providing greater trust.
- Ease of obtaining specific IPs: VPN providers have thousands of servers in various countries, making it easy to obtain an IP from a specific location.
- Advanced encryption: The high-level encryption offered by VPN providers ensures that no data is exposed to leakage risks.
- Specialized servers: Some providers offer servers with additional functionalities, such as Double VPN, Onion Over VPN, and obfuscated servers.
❌ Disadvantages of a VPN
- High cost: Premium VPN providers that offer the best speeds and features are generally more expensive.
- Reliability: The effectiveness of a VPN depends on the reliability of the provider. Free VPNs are rarely secure or reliable.
- Independent audits: Not all VPN providers undergo independent “No logs” audits, which can be a risk factor.
VPN with 75% discount + 3 extra months
CHECK IT OUT →
Comparison: Tor vs. VPN
- Speed: Premium VPNs generally offer higher connection speeds compared to Tor.
- Anonymity: Tor offers a more robust level of anonymity and allows access to the Dark Web.
- Ease of use: VPNs are easier to set up and use to obtain specific IPs and secure the connection on public networks.
- Combination of tools: It is possible to use Tor and VPN simultaneously to increase security, although this reduces connection speed.
Use Cases
- Tor: Ideal for journalists, activists, and users who need extreme anonymity and access to the Dark Web.
- VPN: Preferred by regular users who want to protect their online identity and avoid risks when using public networks.
Choosing the Best Option for You
- Specific needs: Determine your priorities, such as speed, anonymity, or access to the Dark Web.
- Budget: Consider the cost of premium VPN services.
- Security: Evaluate the importance of independent audits and “No logs” policies.

Case Study: NordVPN
NordVPN is an example of a premium VPN provider that offers a wide range of features to ensure user security and privacy.
Among its main features are:
- Multiple device connections: Support for up to 10 devices simultaneously.
- Advanced encryption: Uses AES with 256-bit keys, providing high security.
- Various protocols: Offers OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, and NordLynx.
- Servers in various locations: More than 6000 servers in 100+ locations around the world.
- Customer support: Available 24/7 to resolve any queries.
- Specialized servers: Include options like Double VPN, Onion Over VPN, and obfuscated servers.
- Threat protection: Blocking malicious sites, ads, and trackers.
- Meshnet: Allows connection between devices in private, encrypted tunnels.
Ensure your security with the leading VPN
👉 NORDVPN ON SALE THIS WEEK →
Conclusion
Both Tor and VPN are valuable tools for protecting online privacy.
The choice between one and the other will depend on your specific needs for security, anonymity, and accessibility.
For an ideal combination of speed, ease of use, and robust security, using a premium VPN is generally recommended. However, for access to the Dark Web and extreme anonymity, Tor is the right choice.
As a partner of NordVPN, we may earn a commission if you make purchases through our links—at no extra cost to you. Learn more.